We've had a makeover! There are plenty of reasons to be excited for the new Prolifics Blog. Better design, greater search functionalities and increased reach to name a few. Best of all, our blog is now fully integrated on the Prolifics website, delivering a more seamless experience for our readers.
Please visit us at: www.prolifics.com/blog
We look forward to connecting with you through our new blog!
Tuesday, November 18, 2014
Tuesday, October 21, 2014
HIPAA Compliance: A Document Management Approach
Key Healthcare Challenge:
To comply with Compliance for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
HIPAA Background:
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and its enabling regulations, ensures patient information and records are protected and maintain their integrity.
This requires healthcare organizations to control the use and access to a patient’s private identity and medical information.
HIPAA defines regulations for:
Document Management for Electronic Medical Records
Implementation:
ROI:
What does it mean to all healthcare organizations?
Regardless of where patient information originates - scanned from hard copy, faxed, e-mailed, PC-based or mainframe-based - Document Management Software solutions provides a secure repository that can track all aspects of patient information.
Ritesh Sujir is a Delivery Manager in the Testing Practice at Prolifics. He is an accomplished project management professional with 14+ years of experience working with Fortune 500 clients. Ritesh specializes in all aspects across project management and is accountable for the development and maintenance of project plans, risk assessments, and status reports. His recent experience includes clients in the Banking, Retail, and Healthcare verticals.
To comply with Compliance for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
HIPAA Background:
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and its enabling regulations, ensures patient information and records are protected and maintain their integrity.
This requires healthcare organizations to control the use and access to a patient’s private identity and medical information.
HIPAA defines regulations for:
- Electronic healthcare transactions
- Health information privacy
- Security requirements
- Unique identification for providers
- Unique identification for health plans
- Enforcement procedures
Document Management for Electronic Medical Records
Implementation:
- Simple and easy to implement
- Replaces paper patient records and archives with immediate ROI
- Enables physicians to maintain current work practices:
- Does NOT require any menu-driven patient information input workflows
- Can use current paper-based note taking during office visits
- Provides flexibility to access patient charts immediately at remote locations
- Can also be implemented in concert with a formal EMR system
- Link external information (lab reports, correspondence from specialists, signed consent forms) to EMR records
- Security
- Audit trail
- Reporting
- Electronic Payment Standardization
ROI:
- Access and quality of care: users report very significant gains in fast access to patient information.
- Reduce costs associated with copying and retrieving health information.
- Ensure aspects of system are compliant.
- Health information is more tightly controlled, while at the same time more accessible to those who need it.
- Data is protected.
- Flexible and Scalable
- Small Medical Practice Applications:
- Electronic patient records
- Billing, insurance EOB
- Personnel records
- Hospital Applications:
- Patient records and consent forms linked to EMR system
- Accounts Payable
- Billing
- HR and credentialing
- Purchasing and supply chain
What does it mean to all healthcare organizations?
Regardless of where patient information originates - scanned from hard copy, faxed, e-mailed, PC-based or mainframe-based - Document Management Software solutions provides a secure repository that can track all aspects of patient information.
Ritesh Sujir is a Delivery Manager in the Testing Practice at Prolifics. He is an accomplished project management professional with 14+ years of experience working with Fortune 500 clients. Ritesh specializes in all aspects across project management and is accountable for the development and maintenance of project plans, risk assessments, and status reports. His recent experience includes clients in the Banking, Retail, and Healthcare verticals.
Tuesday, October 14, 2014
The Case for Penetration Testing
Overview
Penetration Testing is the method of testing that focuses on finding areas of weakness in software systems in terms of security. These areas are put to the test to determine if they can be broken into or not.
A penetration test is a proactive and authorized attempt to evaluate the security of an IT infrastructure by safely attempting to exploit system vulnerabilities, including OS, service and application flaws, improper configurations, and even risky end-user behavior. Such assessments are also useful in validating end-users’ adherence to security policies.
The fundamental purpose of penetration testing is to measure the feasibility of systems or end-user compromise and evaluate any related consequences such incidents may have on the involved resources or operations.
Penetration Testing is the method of testing that focuses on finding areas of weakness in software systems in terms of security. These areas are put to the test to determine if they can be broken into or not.
A penetration test is a proactive and authorized attempt to evaluate the security of an IT infrastructure by safely attempting to exploit system vulnerabilities, including OS, service and application flaws, improper configurations, and even risky end-user behavior. Such assessments are also useful in validating end-users’ adherence to security policies.
The fundamental purpose of penetration testing is to measure the feasibility of systems or end-user compromise and evaluate any related consequences such incidents may have on the involved resources or operations.
Reason for Penetration Testing
- Security breaches and service interruptions are costly
- Security breaches and any related interruptions in the performance of services or applications can result in direct financial losses, threaten organizations’ reputations, hamper customer loyalties, and trigger significant fines and penalties.
- Identifies and prioritizes security risks
- Penetration testing evaluates an organization’s ability to protect its networks, applications, endpoints and users from external or internal attempts to circumvent its security controls to gain unauthorized or privileged access to protected assets.
When Should Penetration Testing be Performed?
Penetration testing should be performed on a regular basis to ensure more consistent IT and network security management by revealing how newly discovered threats or emerging vulnerabilities may potentially be assailed by attackers. Tests should also be run whenever:
- New network infrastructure or applications are added
- Significant upgrades or modifications are applied to infrastructure or applications
- New office locations are established
- Security patches are applied
- End user policies are modified
Benefits of Penetration Testing
- Intelligently Manage vulnerabilities
- Avoid the cost of downtime
- Meet Regulatory requirements and avoid fines
- Preserve customer loyalty and corporate image
How to Conduct Penetration Testing
- It starts with a list of Vulnerabilities/potential problem areas that would cause a security breach for the systems.
- If possible, this list of items has to be ranked in the order of priority/criticality.
- Devise penetration tests that would work (attack your system) from both within the network and outside (externally) to determine if you can access data/network/server/website unauthorized.
- If the unauthorized access is possible, the system has to be corrected and the series of steps need to be re-run until the problem area is fixed.
Criteria for Selecting the Best Penetrating Tool
- It should be easy to deploy, configure and use.
- It should scan your system easily.
- It should categorize vulnerabilities based on severity that needs immediate fix.
- It should be able to automate verification of vulnerabilities.
- It should re-verify exploits found previously.
- It should generate detailed vulnerability reports and logs.
Some of Tools Used for Penetration Testing
- Metasploit
- This is the most advanced and popular Framework that can be used to for pen-testing. It is based on the concept of ‘exploit’ which is a code that can surpass the security measures and enter a certain system. If entered, it runs a ‘payload’, a code that performs operations on a target machine, thus creating the perfect framework for penetration testing.
- It can be used on web applications, networks, servers etc. It has a command-line and a GUI clickable interface, works on Linux, Apple Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows.
- WireShark
- This is basically a network protocol analyzer –popular for providing the minutest details about your network protocols, packet information, decryption etc. It can be used on Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and many other systems. The information that is retrieved via this tool can be viewed through a GUI, or the TTY-mode TShark utility.
- Core Impact
- CORE Impact Pro can be used to test mobile device penetration, network/network devise penetration, password identification and cracking, etc. It has a command-line and a GUI clickable interface, works Microsoft Windows. This is one of the expensive tools in this line and all the information can be found at below page.
Conclusion
Penetration testing must be performed to manage
- Intelligently Manage vulnerabilities
- Avoid the cost of downtime
- Meet Regulatory requirements and avoid fines
To learn more about Prolifics' testing solutions, visit: http://www.prolifics.com/solutions/quality-assurance-testing
Ritesh Sujir is a Delivery Manager in the Testing Practice at Prolifics. He is an accomplished project management professional with 14+ years of experience working with Fortune 500 clients. Ritesh specializes in all aspects across project management and is accountable for the development and maintenance of project plans, risk assessments, and status reports. His recent experience includes clients in the Banking, Retail, and Healthcare verticals.
Tuesday, September 30, 2014
The Key to a Successful ECM Solution
Without intending to diminish the features of ECM, I think it's important that we recognize that most of what we rely on for content management and document management is the solution that wraps around the core capabilities of ingestion, extraction, storage, rendition, metadata, classification, retention, and workflow within ECM platforms. In the vast majority of solutions, the user experience is not driven by the ECM core capabilities. It's delivered by a business activity aligned user interface that supports a work task with the content, metadata, and workflow necessary to get the job done.
In the solution narrative, business users are so important that they get forgotten. Establishing an ECM platform can be a sizable investment, and the temptation is to aim for generic user interfaces and start by pushing out of the box capabilities onto users. When that works, I'm all for it! ECM can be done on a configuration basis, and new UIs like Content Navigator do so much more than prior front ends were capable of. Unfortunately, that doesn't work very often.
The reality of our world - or so my selection of specific smartphone apps informs me - is that successful adoption is tied to a user experience first. Capability is the second factor. Reliability is the third. What came out of the box is pretty much an infrastructure concern, and most users are happily unaware of the underpinnings and the technology that they rely on unless it breaks down too often or they lose their data or it requires a manual to use.
Solutions leverage ECM. ECM out of the box is not, per se, a solution. There's so much more we can do with the digital paper trail of our organizations. We do that by enabling the business solution with ECM and enhancing the business capabilities with the content and metadata and content initiated workflows within ECM. Out of the box is great when it comes to delivering the engine, transmission, and chassis. Business users get excited when you bolt on the rest so they can go for a drive.
In the solution narrative, business users are so important that they get forgotten. Establishing an ECM platform can be a sizable investment, and the temptation is to aim for generic user interfaces and start by pushing out of the box capabilities onto users. When that works, I'm all for it! ECM can be done on a configuration basis, and new UIs like Content Navigator do so much more than prior front ends were capable of. Unfortunately, that doesn't work very often.
The reality of our world - or so my selection of specific smartphone apps informs me - is that successful adoption is tied to a user experience first. Capability is the second factor. Reliability is the third. What came out of the box is pretty much an infrastructure concern, and most users are happily unaware of the underpinnings and the technology that they rely on unless it breaks down too often or they lose their data or it requires a manual to use.
Solutions leverage ECM. ECM out of the box is not, per se, a solution. There's so much more we can do with the digital paper trail of our organizations. We do that by enabling the business solution with ECM and enhancing the business capabilities with the content and metadata and content initiated workflows within ECM. Out of the box is great when it comes to delivering the engine, transmission, and chassis. Business users get excited when you bolt on the rest so they can go for a drive.
Mid-Level Company Mobility Program - iOS or Android?
Case at Hand:
A mid-sized company with a workforce of 500+ employees, out of which 40-60% are stationed at client locations more than 50% of the working hours. The company wants to provide a mobile platform to keep the employees connected at all times. With BB on its way to decline, the company decides to establish a new mobile computing platform for its employees, along with a BYOD support option, provided the mobile device is compatible with the company network and user has complete documentation supporting his/her proof of purchase etc.
Evaluating the various options, the company IT admins should look into the following factors here:
Getting the Work Done:
Both android iOS supports MS Exchange accounts, android even has the meeting invite response.
Both android and iOS support MS office. There are multiple 3rd party app providers for working with MS office on both leading mobile platform. Google recently even release Google Docs, Sheet and Slides – which have the native capability to edit the MS office 3 most important formats – Word, Excel and PowerPoints, and that too for free! Also google drive provides a large cloud drive for free which can be used for free and seamlessly integrates with Google’s office solutions. So, a ‘+1’ for android in this department.
Network Support for Admins:
This is important – as there is a BYOD option that the company wants to explore. However if the company decides to go with android instead of iOS, the network admins are sure to have a tough time due to android fragmentation. Even if most of the android users are on KitKat (4.2+), the various UI customizations by the OEMs can still create nightmares for the admins trying to troubleshoot device related issues over a call. Here the iOS scores +1 due to vertical integration between software and hardware and minimal fragmentation and more or less the same UI over all iOS devices.
Security:
Both android and iOS provides robust security with device encryption and remote wipe features. iOS maintains an edge here as android devices are easier to unlock bootloader and obtain ‘root’. It’s also easier to ‘sideload’ applications in android than in iOS which can be security admin nightmare.
Also starting from iOS 8 the device encryption will be switched on by default. Starting with Android L google is rumored to keep android device encryption switched on by default which will give it added protection. However despite all this, the perception of security in iOS is more than that of android as it had issues of malware infections in the past through the official Google Play Store. Due to fingerprint scanner present on all newer iOS devices, iOS gains one more +1 here.
Cloud Implementation:
Google’s cloud services are much robust than apple’s which is just foraying into the cloud area with its iCloud initiatives. Android can use enterprise J2EE backend services, whereas iOS is a bit limited in scope in this area. Hence developer support can be better for android than iOS due to the popularity with J2EE framework. +1 for android here
Killer Apps:
For many Google maps and Google Now are two killer apps that overshadow the apple maps / Siri by a large margin. Google seamless integration of data across its multiple services results in a much powerful contextual device. Regarding other apps, google and Apple are almost tied as both platforms carry almost all the required apps by developers. The android emulator is supposed to be one of the best and hence app development is a breeze. +1 for Android here.
Conclusion:
Office work – Google
Network admin – iOS
Security – iOS
Cloud implementation – Google
Apps / Solutions – Google
The company management should allocate weights to the various parameters and evaluate the costs associated with network administration of each platform. As of now both platforms are quite competitive and provide their own sets of value addition and challenges for a company-wide BYOD program.
A mid-sized company with a workforce of 500+ employees, out of which 40-60% are stationed at client locations more than 50% of the working hours. The company wants to provide a mobile platform to keep the employees connected at all times. With BB on its way to decline, the company decides to establish a new mobile computing platform for its employees, along with a BYOD support option, provided the mobile device is compatible with the company network and user has complete documentation supporting his/her proof of purchase etc.
Evaluating the various options, the company IT admins should look into the following factors here:
Getting the Work Done:
Both android iOS supports MS Exchange accounts, android even has the meeting invite response.
Both android and iOS support MS office. There are multiple 3rd party app providers for working with MS office on both leading mobile platform. Google recently even release Google Docs, Sheet and Slides – which have the native capability to edit the MS office 3 most important formats – Word, Excel and PowerPoints, and that too for free! Also google drive provides a large cloud drive for free which can be used for free and seamlessly integrates with Google’s office solutions. So, a ‘+1’ for android in this department.
Network Support for Admins:
This is important – as there is a BYOD option that the company wants to explore. However if the company decides to go with android instead of iOS, the network admins are sure to have a tough time due to android fragmentation. Even if most of the android users are on KitKat (4.2+), the various UI customizations by the OEMs can still create nightmares for the admins trying to troubleshoot device related issues over a call. Here the iOS scores +1 due to vertical integration between software and hardware and minimal fragmentation and more or less the same UI over all iOS devices.
Security:
Both android and iOS provides robust security with device encryption and remote wipe features. iOS maintains an edge here as android devices are easier to unlock bootloader and obtain ‘root’. It’s also easier to ‘sideload’ applications in android than in iOS which can be security admin nightmare.
Also starting from iOS 8 the device encryption will be switched on by default. Starting with Android L google is rumored to keep android device encryption switched on by default which will give it added protection. However despite all this, the perception of security in iOS is more than that of android as it had issues of malware infections in the past through the official Google Play Store. Due to fingerprint scanner present on all newer iOS devices, iOS gains one more +1 here.
Cloud Implementation:
Google’s cloud services are much robust than apple’s which is just foraying into the cloud area with its iCloud initiatives. Android can use enterprise J2EE backend services, whereas iOS is a bit limited in scope in this area. Hence developer support can be better for android than iOS due to the popularity with J2EE framework. +1 for android here
Killer Apps:
For many Google maps and Google Now are two killer apps that overshadow the apple maps / Siri by a large margin. Google seamless integration of data across its multiple services results in a much powerful contextual device. Regarding other apps, google and Apple are almost tied as both platforms carry almost all the required apps by developers. The android emulator is supposed to be one of the best and hence app development is a breeze. +1 for Android here.
Conclusion:
Office work – Google
Network admin – iOS
Security – iOS
Cloud implementation – Google
Apps / Solutions – Google
The company management should allocate weights to the various parameters and evaluate the costs associated with network administration of each platform. As of now both platforms are quite competitive and provide their own sets of value addition and challenges for a company-wide BYOD program.
Monday, September 8, 2014
Adding IT Value to Evolving Business Models
Executive Summary:
Change has become the new normal across industries. The healthcare industry is dealing with changing market dynamics and is only now realizing the full impact of the Affordable Care Act. The financial services sector is facing growing regulatory challenges on one side and the opportunities offered by the recovering global economy on the other side. The US retail and B2B banking sector is under the impact of changing customer preferences vis-à-vis mobile banking. US Retailers are also dealing with domestic “low price” challengers and the avenues offered by the investment opportunities in the emerging economies, especially in the e-commerce sector. Manufacturers have the need to optimize the production and supply chains in order to lower costs. This article explores how effective IT decision making could help firms deal with the constant flux in their business models.
Healthcare:
The market dynamics in healthcare is changing, as the firms involved understand the true impact of the Affordable Care Act. There is increased competition because of insurance exchanges and the existing market shares are being disrupted (see exhibit 1).The reimbursement models are being updated, the healthcare networks are evolving and the Medicare market is expanding as more baby boomers retire. Hospitals are revamping their service delivery models to better improve patient outcomes and insurance companies (payers) are trying to negotiate better contracts with hospitals (providers) and formulate the most optimal benefit plans for patients. Under such a scenario, it’s critical for both the payers and providers to understand the evolved preferences of the old and new clients/customers. Do customers prefer a high deductible plan with wide coverage or a low deductible plan with narrow coverage? What type of group insurance are the employers demanding with geographically diversified work force? Are more employees telecommuting to work and if yes, have their insurance needs changed?
The second key aspect is to re-evaluate the firm’s business value. How can I drive better business value in the changed landscape? Are we targeting the correct market segment? Are our plans/benefits still relevant? Are our claim adjudication systems capable of meeting the new SLA’s? After deliberating on the above questions, the firms have to assess the capabilities that need shoring up. Creating a rules based, flexible reimbursement, network, contract and benefit management systems and having a better control of the business processes by automating them will help the insurance companies. Since the changes are continuous, it’s beneficial to set up a Service Oriented Architecture within the enterprise and better integrate the disparate source systems. Firms can deal with changes better when a service oriented enterprise is created.
Exhibit 1:
Change has become the new normal across industries. The healthcare industry is dealing with changing market dynamics and is only now realizing the full impact of the Affordable Care Act. The financial services sector is facing growing regulatory challenges on one side and the opportunities offered by the recovering global economy on the other side. The US retail and B2B banking sector is under the impact of changing customer preferences vis-à-vis mobile banking. US Retailers are also dealing with domestic “low price” challengers and the avenues offered by the investment opportunities in the emerging economies, especially in the e-commerce sector. Manufacturers have the need to optimize the production and supply chains in order to lower costs. This article explores how effective IT decision making could help firms deal with the constant flux in their business models.
Healthcare:
The market dynamics in healthcare is changing, as the firms involved understand the true impact of the Affordable Care Act. There is increased competition because of insurance exchanges and the existing market shares are being disrupted (see exhibit 1).The reimbursement models are being updated, the healthcare networks are evolving and the Medicare market is expanding as more baby boomers retire. Hospitals are revamping their service delivery models to better improve patient outcomes and insurance companies (payers) are trying to negotiate better contracts with hospitals (providers) and formulate the most optimal benefit plans for patients. Under such a scenario, it’s critical for both the payers and providers to understand the evolved preferences of the old and new clients/customers. Do customers prefer a high deductible plan with wide coverage or a low deductible plan with narrow coverage? What type of group insurance are the employers demanding with geographically diversified work force? Are more employees telecommuting to work and if yes, have their insurance needs changed?
The second key aspect is to re-evaluate the firm’s business value. How can I drive better business value in the changed landscape? Are we targeting the correct market segment? Are our plans/benefits still relevant? Are our claim adjudication systems capable of meeting the new SLA’s? After deliberating on the above questions, the firms have to assess the capabilities that need shoring up. Creating a rules based, flexible reimbursement, network, contract and benefit management systems and having a better control of the business processes by automating them will help the insurance companies. Since the changes are continuous, it’s beneficial to set up a Service Oriented Architecture within the enterprise and better integrate the disparate source systems. Firms can deal with changes better when a service oriented enterprise is created.
Exhibit 1:
As the global economy recovers from the financial crisis of 2008, it presents both challenges as well as opportunities. Various regulatory requirements put in place such as Basel III, Dodd Frank Act, Simpson-Bowles Plan etc., to prevent a repeat of the financial crisis force significant changes to the business model of the financial firms. A KPMG study on the impact of regulations on the financial services sector predicts a high impact on the net income of the firms (See exhibit 2). With these regulatory changes, firms have to update their IT systems to better capture critical data. Firms are better off undertaking an effort to optimize their IT infrastructure, overhauling their enterprise application security, enhancing their digital user experience interfaces to capture additional data and migrating and modernizing their IT applications. These efforts could be staggered to prevent disruptions to the everyday business but are very critical to effectively comply with regulatory requirements.
The recovery of the global economy also provides new opportunities for growth to the sector. As new business models are discovered and new market segments identified, the firms have to put in place business processes and rules to capture those segments. Digitizing business processes and rules gives better control to the firms and the required flexibility to deal with any future changes.
Exhibit 2:
Banking:
The new retail and B2B banking customer is increasingly conducting his/her transactions via the mobile application. As per a McKinsey & Co survey, today 65 percent of customers interact with their banks through multiple channels. Human interactions are generally reserved for more complex problems: only 25 percent of agent phone calls are inquiries that could be serviced in other channels. Banks that do not provide the seamless banking experience to customers across various channels – branch, mobile and web – risk the possibility of losing out the customer’s business to other banks that provide a seamless experience. Effective mobile strategy that provides banking value to the customer and also provides banks an ability to cross sell products to the consumer similar to a physical branch is needed. Banks need to adopt cloud mobile development platform such as IBM Worklight to quickly create mobile applications and roll it out to the end consumer.
In a B2B setting, banks that can quickly set up new accounts and add/update financial products to the banking business customer can capture additional market share. The sales representatives should be able to present the product information and capture customer information on a tablet. Designing and selling new financial products that offer convenience to the businesses will provide the competitive edge to the banks.
Retail:
US retailers are being challenged over price by “online only” retailers such as Amazon and other competitors that are offering e-commerce channel. The retailers are struggling to reduce high costs due to big investment in stores. A key method to reduce high inventory costs is to have an integrated supply chain visibility and to be able to sync the merchandize ordering with that of supplier inventories. Also retailers can no longer have fulfillment channels in silos. There is a need to integrate the fulfillment channels and provide visibility across – a consumer should be able to add a desired product to their wish list on the website, review that product in store, purchase the product in store or place an order online and receive the product. The product return procedures should be similar irrespective of where the product was purchased. In order to provide the new business value, the retailers need to transform the customer digital experience, better integrate their source systems and modernize their IT applications by moving them into new platforms.
E-Commerce provides an exciting opportunity in the emerging markets. As per RESEARCHANDMARKETS study, the e-Commerce industry in India is expected to grow at a CAGR of 40%, from US $ 5.9 billion in 2010 to US $ 34.2 billion in 2015E. An India based e-Commerce retailer, Flipkart, recently raised $1 billion in fresh funding. Amazon is increasing its presence in India as well. The emerging middle class of the developing economies provides a huge opportunity for the retailers. The new consumers with disposable income favor purchases of latest technology products, mainly electronic goods, over the internet. There is a significant margin that could be captured here. These new markets provide additional area of growth for those retailers with global ambitions. The retailers should fortify their e-commerce offerings and build a strong supply chain integrated with their e-commerce sites both over the web and mobile. The proliferation of smart phones in emerging economies also provides a huge opportunity in the m-commerce space. The mobile development strategy is critical to capture this opportunity.
Manufacturing:
With increased competition from global competitors, US manufacturers face a growing need to optimize production and reduce costs. It is more critical than ever to identify the core strengths in manufacturing and outsource any parts that are better off supplied by a supplier with a low cost. The manufacturers need to constantly evaluate available supply chain options and choose the most cost effective option. As per a KPMG survey, many manufacturing executives (49 percent globally; 54 percent U.S.) admit that their companies currently do not have visibility of their supply chain beyond Tier 1 suppliers. Moreover, only 9 percent of the 335 global respondents of the 2013 KPMG survey say they have complete visibility of their supply chains. This number is even lower among U.S. executives, with only 7 percent claiming complete supplier visibility (see exhibit 3). Adopting a robust Business Analytics and Decision Management solution is a key lever in the changed landscape. Using a business analytics and reporting software such as IBM Cognos provides the manufacturers with access to real time data on production capacity, inventory management, supplier inventories, budgeting, forecasting etc., so that more informed decisions could be made.
Exhibit 3:
Conclusion:
While updating the business model to better deal with the changing landscape is a challenge, overhauling and effectively implementing an IT ecosystem will help smooth the journey to a great extent. Taking the help of advances in IT will help to reduce the productivity disruptions caused while modifying the current business model. Choosing a trusted IT business partner that can provide holistic IT services will also go a long way in alleviating this pain.
To learn about how Prolifics provides business value to clients around the world, visit www.prolifics.com.
 |
N.R. Vijay is a Solution Architect in the Business Process Management division of Prolifics. He has over 10 years of consulting experience across domains such as Retail, Healthcare and Banking. Specializing in technology, management concepts and enterprise strategy, he is focused on change management and process improvement initiatives. He co-authored a whitepaper titled "Improving Customer Loyalty through Business Process Optimization and Advanced Business Analytics"
 |
Wednesday, August 27, 2014
Achieving Regulatory Compliance with Decision Management
The 2008 financial crisis affected each of us in some manner. In particular, financial institutions and banks felt most of the heat. There were several repercussions of this crisis in the form of increased regulations and various legislation in an effort to curtail such an occurrence in the future. The aim of such regulations is to maintain confidence in the financial system, to increase financial stability, to protect consumers at some level and to reduce financial irregularities.
Since financial institutions now live in a climate of increased compliance and regulation, there has been an increase of consulting firms – both technical and advisory – in providing specialized services to help these institutions implement regulatory compliance so that these institutions can focus on their business while complying with these ever changing regulations.
It would be futile to jump into a solution of how this can be achieved without understanding what regulatory compliance means. Compliance means conforming to a rule which can be a policy, standard or law. Regulatory Compliance describes the goal that companies aspire to achieve in order to comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Where do business rules fit in the picture?
Business rules are by definition a statement that describes the policies or constraints of an organization. Since compliance requires conforming to a policy in general, business rules fit the perfect picture as a placeholder of such policies. This is for various reasons. First, rules are repeatable and tractable to automation. Second, rules are transparent and easily traceable. This makes for increased visibility of the policies which are to be complied with. Business rules implemented with IBM’s Operational Decision Management software can be exported to a word or excel document, and even be emailed to an organization’s legal department in the format they are written. Third, rules can be changed easily with zero down time to make the change to production. This helps organizations cope with an ever-changing regulatory environment and allow them to focus on its business rather than inviting preseason resources keeping up with a changing regulatory environment.
How can regulatory compliance be achieved by Operational Decision Management (ODM)?
The best way to describe ODM’s capabilities for regulatory compliance would be to take existing compliance policies that firms have to constantly deal with, and propose an implementation using ODM. We take one of the most challenging regulations that was recently (2010) enacted by the 111th US Congress – it is the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act or more popularly known as FATCA. The act aims to tackle tax evasion by US Citizens to tax havens or strong data protection countries like Switzerland. Foreign financial institutions like banks, insurance firms and fund houses are affected by FATCA and need to comply with FATCA regulations. Individuals with US nationality, US address or phone number and corporations with substantial US ownership are affected by this legislation. Complying with FATCA became so complex and necessary at the same time that IBM has offered a specialized FATCA solution in their offerings.
One of the challenges FATCA brings is the amount of information it requires an organization to process which especially creates a hassle to the organization’s technology platform. There are three different impacts to the technology platform with FATCA – customer classification, transaction monitoring and finally IRS reporting.
In our business case example, let us study customer classification. In order to comply with FATCA, financial organizations have to collect a W-9 form from all account holders who are US Persons. This is clearly business logic which can take an ugly and complex turn when implemented in application code. The solution: WebSphere Operational Decision Management (ODM). The above business logic can be copied word to word and represented in the form of a business rule. It can be created in what is called a rule designer. This is how the same business logic looks like when written in ODM as a business rule:
The above business rule can be exported as-is to what is called the decision center which is the special portal that business users have access to with the ODM suite of products. Decision Center gives immense visibility to the rules across an organization. Major stakeholders can log in to this portal and view the contents of critical decision tables or business rules. Returning to our scenario above, the same FATCA rule when deployed to the decision center, can be edited by business users by click of a button. Clicking on the “Edit” link below, the rule can be easily modified by a non-technical user:
Since financial institutions now live in a climate of increased compliance and regulation, there has been an increase of consulting firms – both technical and advisory – in providing specialized services to help these institutions implement regulatory compliance so that these institutions can focus on their business while complying with these ever changing regulations.
It would be futile to jump into a solution of how this can be achieved without understanding what regulatory compliance means. Compliance means conforming to a rule which can be a policy, standard or law. Regulatory Compliance describes the goal that companies aspire to achieve in order to comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Where do business rules fit in the picture?
Business rules are by definition a statement that describes the policies or constraints of an organization. Since compliance requires conforming to a policy in general, business rules fit the perfect picture as a placeholder of such policies. This is for various reasons. First, rules are repeatable and tractable to automation. Second, rules are transparent and easily traceable. This makes for increased visibility of the policies which are to be complied with. Business rules implemented with IBM’s Operational Decision Management software can be exported to a word or excel document, and even be emailed to an organization’s legal department in the format they are written. Third, rules can be changed easily with zero down time to make the change to production. This helps organizations cope with an ever-changing regulatory environment and allow them to focus on its business rather than inviting preseason resources keeping up with a changing regulatory environment.
How can regulatory compliance be achieved by Operational Decision Management (ODM)?
The best way to describe ODM’s capabilities for regulatory compliance would be to take existing compliance policies that firms have to constantly deal with, and propose an implementation using ODM. We take one of the most challenging regulations that was recently (2010) enacted by the 111th US Congress – it is the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act or more popularly known as FATCA. The act aims to tackle tax evasion by US Citizens to tax havens or strong data protection countries like Switzerland. Foreign financial institutions like banks, insurance firms and fund houses are affected by FATCA and need to comply with FATCA regulations. Individuals with US nationality, US address or phone number and corporations with substantial US ownership are affected by this legislation. Complying with FATCA became so complex and necessary at the same time that IBM has offered a specialized FATCA solution in their offerings.
One of the challenges FATCA brings is the amount of information it requires an organization to process which especially creates a hassle to the organization’s technology platform. There are three different impacts to the technology platform with FATCA – customer classification, transaction monitoring and finally IRS reporting.
In our business case example, let us study customer classification. In order to comply with FATCA, financial organizations have to collect a W-9 form from all account holders who are US Persons. This is clearly business logic which can take an ugly and complex turn when implemented in application code. The solution: WebSphere Operational Decision Management (ODM). The above business logic can be copied word to word and represented in the form of a business rule. It can be created in what is called a rule designer. This is how the same business logic looks like when written in ODM as a business rule:
Any changes to these business rules in general can be directly deployed to production environment, through the decision center portal. Obviously, there are various recommended governance strategies that provide checks and balances along with regression testing, so that incorrect information is not pushed to production servers. Nevertheless, the capability to change an existing policy (or a decision table) is available with ODM.
Conclusion
Regulations are here to stay and the sooner organizations adapt to implement compliance with these regulations, the better they will become for their competition. In our example for FATCA we just saw how ODM can be leveraged to implement changes at a lightning pace. There is much more that can be achieved with ODM, this just gives a small glimpse of what your organization can look forward to when selecting ODM as a solution to meet your organization’s compliance.
Tuesday, August 26, 2014
Testing Philosophy in ODM: Feasibility of Complete Rule Testing in Decision Validation Services (DVS)
Software testing is an important step in the software development life cycle. IBM Operational decision Management (ODM) is not an exception. Testing in ODM is done through Decision Validation Services (DVS). It automatically generates an excel sheet with specified input fields from the Execution Object Model (XOM). To run a test you need to fill out the excel sheet with test cases and expected outputs. Each row would represent a test case. In this article I would like to discuss the feasibility of running a complete (or close to complete) test in DVS based on the number of fields and the complexity of the decision (rules).
Let us first consider the feasibility of complete test regardless of the technology/software choice. For simplicity let us consider rules around only three fields (Field1, Field2, Field3), which carry binary values. The maximum number of test cases needed to run a complete test for the ruleset is 2^3=8.
This is a simple example (n=3), but it can help us visualize and understand how to handle the test cases with a lot more fields/elements. Note: 2^3=8 is also the maximum number of unambiguous rules that can be implemented with 3 fields. This can also be visualized as a binary tree. The height represents the number of fields and the leaves of the tree represent the rules. E.g. the left most leaf R1 corresponds to the rule#1 in the above table (F1=true and F2=true and F3=true).
Let us first consider the feasibility of complete test regardless of the technology/software choice. For simplicity let us consider rules around only three fields (Field1, Field2, Field3), which carry binary values. The maximum number of test cases needed to run a complete test for the ruleset is 2^3=8.
#
|
Field1
|
Field2
|
Field3
|
Ruleset Output
|
1
|
T
|
T
|
T
|
|
2
|
T
|
T
|
F
|
|
3
|
T
|
F
|
T
|
|
4
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
|
5
|
F
|
T
|
T
|
|
6
|
F
|
T
|
F
|
|
7
|
F
|
F
|
T
|
|
8
|
F
|
F
|
F
|
This is a simple example (n=3), but it can help us visualize and understand how to handle the test cases with a lot more fields/elements. Note: 2^3=8 is also the maximum number of unambiguous rules that can be implemented with 3 fields. This can also be visualized as a binary tree. The height represents the number of fields and the leaves of the tree represent the rules. E.g. the left most leaf R1 corresponds to the rule#1 in the above table (F1=true and F2=true and F3=true).
In general for N fields, each of which can take K values (group of values), there can be at most K^N unambiguous rules implemented. In the above example N=3 and K=2 (binary fields). We can generalize it even further. There can be fields with different number of accepted values (group of values). If there are n fields, each of which can take k values and there are m fields each of which can take p values, there can be at most k^n* p^m unambiguous rules implemented.
Another philosophical question we should ask is how much testing is sufficient. E.g. if we have implemented R1,R2,R3, do we have to implement test cases for the tracks R4, R5, R6, R7,R8 , i.e. do we have to prove that unimplemented rules did not fire(unintentionally)?!?! The answer is - it depends!! We may have to do 1 or 2 test cases for unimplemented rules, depending on the complexity of the rules. Example: loan approval application that has a rule: “if the age of the applicant is greater than 40 and the credit score is “good” then approve”. If we were to write test cases for that single rule, we might have to do the following:
#
|
Age is greater than 40
|
Credit score is “good”
|
Expected output
|
1
|
T
|
T
|
Approve
|
2
|
T
|
F
|
The default approval status
|
Theoretically we did not “have to” do the second test case, but it is good to make sure the approval is set by the implemented rules and not by some bug that sets it to “approve” regardless of rule conditions.
What if there were 100 fields instead and let us keep them binary for simplicity (would not change the problem if they could accept 3, 4, 5 ... n values). The max number of rules constructed and the max number of test cases need to do a complete case is 2^100.
#
|
Field1
|
Field2
|
…
|
Field100
|
Ruleset Output
|
1
|
T
|
T
|
T
|
||
2
|
T
|
T
|
F
|
||
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
||
F
|
F
|
F
|
Often times we implement rules with more than 100 XOM elements and to run a complete test we would need 2^100~1.27*〖10〗^30test cases. Theoretically this is an unfeasible problem if we consider the worst case scenario.
The number of fields is relevant only in theoretical discussion, considering the worst cases (2^n , where n is the number of fields). In practice though the number of test cases is needed for DVS is equal or comparable to the number of rules. That means that if it was feasible to create N number of rules, then it would be feasible to implement sufficient test cases for complete testing in DVS.
To learn more about Prolifics' ODM solutions, visit our website or contact solutions@prolifics.com.
Tuesday, July 29, 2014
Customers Purchase Benefits, Not Products
Business organizations have core competency in certain areas and are more likely to have strong capabilities in those areas. Firms are also likely to look for outside consultants in areas where they do not have enough home grown talent and more likely to outsource capabilities such as IT in case of an internal gap. This article is a quick overview of some of the decision challenges faced by the firms while trying to decide what capabilities to outsource.
Businesses are facing a challenging landscape. The customer is connected and empowered. The customer can compare healthcare insurance plans at the click of a button. He or she can search for the best price for consumer goods online and order it online to have it delivered the same day. The customer is purely shopping for benefits while the firms are selling products/services to provide those benefits. Consumer needs have changed, since they are exposed to products from across the globe. A customer's access to information is unbound, thanks to internet. This has resulted in firms re-evaluating their business model to see if they are still serving the evolving customer needs. An insurance company offering high deductible plans with a wide coverage might no longer be relevant in a new target market. The new market demand, due to changing demographics, might be for lower deductibles with a smaller specialist network. An historically well-performing video game with MP3 song playing capabilities might no longer be relevant because of the availability of music on smartphones.
Under such scenarios, the firm has to re-think its business model and make key decisions about how best to leverage its existing capabilities to meet the new market demands. After the firm has decided to revamp its product/service to best meet the new consumer needs, it has to review its existing capabilities - human resource capabilities, IT capabilities, supplier capabilities etc. Because of the competitive landscape, the time to market for modified products/services has to be very short. Productivity of its employees becomes critical in order to achieve high speed to market. IT systems play a key role in increasing the productivity of a firm's employees. During the process of selecting a suitable IT product, the firms have to select a product that best compliments its employees’ skills. Not every "out of the shelf" product will meet the needs of the firms. Especially since the changing business needs require updated employee skills, it is rare for "off-the-shelf" products to meet the new needs of the firms exactly. The IT products needs to be customized to the needs of the firms. Under such a scenario, it is critical for the firms to engage with IT product & consulting companies that have worked with firms from various industries and effectively understand the changing needs of its clients. Firms such as IBM have worked with clients from various industries for a long time and collected extensive domain knowledge. This knowledge is helping IBM and other firms in its ecosystem to quickly develop products and solutions to effectively deal with the emerging challenges. IBM products such as IBM BPM 8. X (Business Process Manager), Cognos, ODM (Operations Decision Management) carry with them an history of experience with business clients with evolving needs. This experience has resulted in development of features that are applicable and adaptable to various business needs. E.g.: The business process design and integration capabilities are as adaptable to a retailers in-house legacy mainframe systems as they are adaptable to a newly on-boarded supplier’s web services. Cognos data analytics capabilities can “talk” to an insurance firm’s legacy data source systems as well as capture real time data generated by the process.
When the time to market is so short, it might be difficult for firms to build the IT capabilities in-house. Firms are more likely to benefit from outsourcing IT development in areas where the internal employees have not yet matured at. Besides, the key upside of outsourcing an IT skill is quick development of IT applications and helping in the final goal of delivering a firms product/ service to market faster. Before making the decision to choose an IT consulting firm, the business firm has to evaluate the client portfolio of the IT consulting firm, it's nature of projects implemented historically and breadth of domain expertise. IT consulting firms that have worked with key players in a particular industry have better exposure to industry challenges. Consultants that have a shorter learning curve will achieve higher productivity while helping to design and build an suitable IT application.
Bottom Line: When businesses choose the right, flexible IT application and partner with consultants with right skills, they increase their chances of effectively catering the evolving needs of their customers.
Businesses are facing a challenging landscape. The customer is connected and empowered. The customer can compare healthcare insurance plans at the click of a button. He or she can search for the best price for consumer goods online and order it online to have it delivered the same day. The customer is purely shopping for benefits while the firms are selling products/services to provide those benefits. Consumer needs have changed, since they are exposed to products from across the globe. A customer's access to information is unbound, thanks to internet. This has resulted in firms re-evaluating their business model to see if they are still serving the evolving customer needs. An insurance company offering high deductible plans with a wide coverage might no longer be relevant in a new target market. The new market demand, due to changing demographics, might be for lower deductibles with a smaller specialist network. An historically well-performing video game with MP3 song playing capabilities might no longer be relevant because of the availability of music on smartphones.
Under such scenarios, the firm has to re-think its business model and make key decisions about how best to leverage its existing capabilities to meet the new market demands. After the firm has decided to revamp its product/service to best meet the new consumer needs, it has to review its existing capabilities - human resource capabilities, IT capabilities, supplier capabilities etc. Because of the competitive landscape, the time to market for modified products/services has to be very short. Productivity of its employees becomes critical in order to achieve high speed to market. IT systems play a key role in increasing the productivity of a firm's employees. During the process of selecting a suitable IT product, the firms have to select a product that best compliments its employees’ skills. Not every "out of the shelf" product will meet the needs of the firms. Especially since the changing business needs require updated employee skills, it is rare for "off-the-shelf" products to meet the new needs of the firms exactly. The IT products needs to be customized to the needs of the firms. Under such a scenario, it is critical for the firms to engage with IT product & consulting companies that have worked with firms from various industries and effectively understand the changing needs of its clients. Firms such as IBM have worked with clients from various industries for a long time and collected extensive domain knowledge. This knowledge is helping IBM and other firms in its ecosystem to quickly develop products and solutions to effectively deal with the emerging challenges. IBM products such as IBM BPM 8. X (Business Process Manager), Cognos, ODM (Operations Decision Management) carry with them an history of experience with business clients with evolving needs. This experience has resulted in development of features that are applicable and adaptable to various business needs. E.g.: The business process design and integration capabilities are as adaptable to a retailers in-house legacy mainframe systems as they are adaptable to a newly on-boarded supplier’s web services. Cognos data analytics capabilities can “talk” to an insurance firm’s legacy data source systems as well as capture real time data generated by the process.
When the time to market is so short, it might be difficult for firms to build the IT capabilities in-house. Firms are more likely to benefit from outsourcing IT development in areas where the internal employees have not yet matured at. Besides, the key upside of outsourcing an IT skill is quick development of IT applications and helping in the final goal of delivering a firms product/ service to market faster. Before making the decision to choose an IT consulting firm, the business firm has to evaluate the client portfolio of the IT consulting firm, it's nature of projects implemented historically and breadth of domain expertise. IT consulting firms that have worked with key players in a particular industry have better exposure to industry challenges. Consultants that have a shorter learning curve will achieve higher productivity while helping to design and build an suitable IT application.
Bottom Line: When businesses choose the right, flexible IT application and partner with consultants with right skills, they increase their chances of effectively catering the evolving needs of their customers.
 |
N.R. Vijay is a Solution Architect in the Business Process Management division of Prolifics. He has over 10 years of consulting experience across domains such as Retail, Healthcare and Banking. Specializing in technology, management concepts and enterprise strategy, he is focused on change management and process improvement initiatives. He co-authored a whitepaper titled "Improving Customer Loyalty through Business Process Optimization and Advanced Business Analytics"
 |
Thursday, July 24, 2014
4 Steps to Risk-Based Software Testing
Risk-based testing is the approach that allows us to plan our testing efforts in a way that reduces the residual level of product risk when the system is deployed. A risk-based approach helps you to understand the risks at the initial stage so that the mitigation strategy will be scheduled and implemented. Test effectiveness indicates the level of effort that is required in order to mitigate the risk of implementing a change. The higher the test effectiveness required, the more rigorous the test and evaluation activities should be. The following factors are used in determining the required test effectiveness:
Impact refers to the potential damage that the business might suffer if the intended functionality is not delivered. When assessing impact, the chances of the change negatively affecting other functions/features are not considered as that is captured under a separate attribute (Regression). The higher the impact, the more rigorous the tests should be. For example, if a simple report is being implemented and is used by only few users, then the potential damage would be minimal and therefore the impact assessment should result in a rating of ""min"".
The following checkpoints should be considered when assigning a rating for the impact factor:
2. Determine probability of failure by analyzing: (1. Min, 2. Low, 3. Medium, 4. High, 5. Severe)
Probability of failure is an assessment of overall risk-based on various consideration like the complexity of the solution, ambiguity in requirements, complex logic etc. The following checkpoints should be considered when assigning a rating for complexity:
3. Determine Regression Impact (1. Min, 2. Low, 3. Medium, 4. High, 5. Severe)
Regression impact is the impact to the existing business processes and functions and is weighted very heavily in terms of the overall determination of the test effectiveness required. This is also the most important focus of the service validation and test group.
4. Determine Recovery Effort/Difficulty from Potential Failure (1. Min, 2. Low, 3. Medium, 4. High, 5. Severe)
When determining the test effectiveness required to mitigate the risk of the change, the ability to recover from a potential failure needs to be considered. Even if a failure occurs, if recovery is possible quickly, then the risk is mitigated to an extent. However, if recovery is very difficult then the test effectiveness needs to be high if the solution component is critical to operations.
Risk Based Testing – An Example:
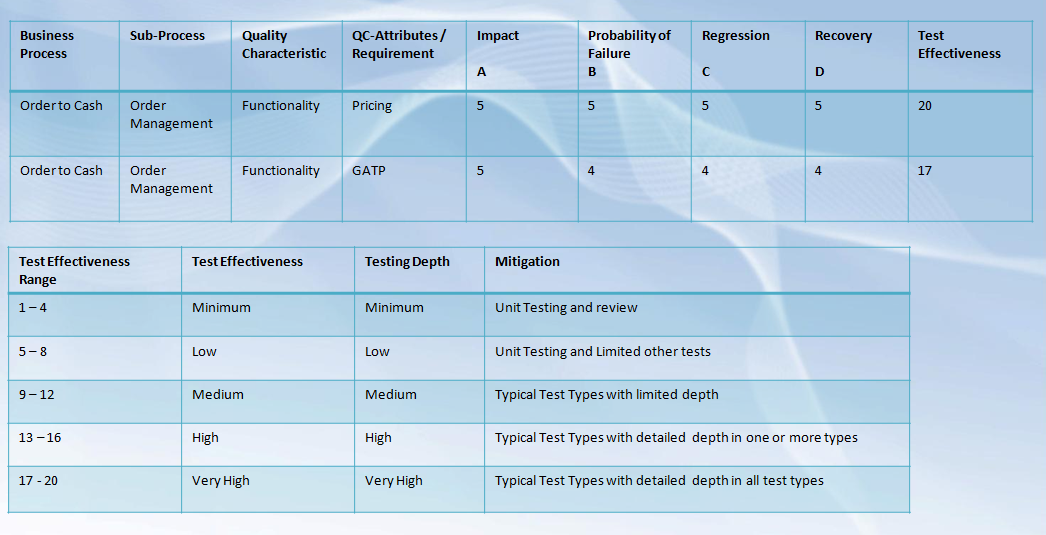
Prolifics specializes in providing end-to-end testing and test automation solutions that are backed by a unique service framework, proven test accelerators and one of the highest defect removal efficiency rate in the industry. Our highly skilled team of testing specialists help to enhance IT productivity and improve application quality, saving millions of dollars through early detection and scope coverage.
To learn more, visit http://www.prolifics.com/quality-assurance-testing.
- Impact
- Probability of Failure
- Regression
- Recovery
Impact refers to the potential damage that the business might suffer if the intended functionality is not delivered. When assessing impact, the chances of the change negatively affecting other functions/features are not considered as that is captured under a separate attribute (Regression). The higher the impact, the more rigorous the tests should be. For example, if a simple report is being implemented and is used by only few users, then the potential damage would be minimal and therefore the impact assessment should result in a rating of ""min"".
The following checkpoints should be considered when assigning a rating for the impact factor:
- A. Is the solution component a primary function/feature of the solution (i.e. must have vs. Nice to have)?
- B. Is the solution component independent or other business processes dependent on it?
- C. Does the data pertaining to transactional volume, financial and other operational considerations indicates significant utility?
- D. Is the Solution component used by important stakeholders (Large customers, Regulatory etc.)
- E.Is the impact to external stakeholders or Internal?
- F.Is the impact to a single business unit vs. multiple business unit?
- G. Number of stakeholders/users that might be impacted?
- H. Impacts based on implementation and roll out strategy. For example, some process may not be executed immediately after implementation
- I. How frequently is the solution component used?
- J. Real time vs. Batch (Real time generally leads to immediate impacts and therefore more risky)
2. Determine probability of failure by analyzing: (1. Min, 2. Low, 3. Medium, 4. High, 5. Severe)
Probability of failure is an assessment of overall risk-based on various consideration like the complexity of the solution, ambiguity in requirements, complex logic etc. The following checkpoints should be considered when assigning a rating for complexity:
- A. Technologies used (New technologies lead to higher risk)
- B. Level of Customization (Higher customization leads to higher complexity)
- C. Complex logic and business rules
- D. Real time vs batch. Real time typically would be more risky as impacts are immediate
- E. Higher defect density as perceived from prior testing engagements
- F. Development effort (The larger the development, the more potential for failure)
- G. Ambiguity in requirements
- H. Complexity of solution
- I. Rushed schedule
- J. Dependency on integration with external systems/partners
3. Determine Regression Impact (1. Min, 2. Low, 3. Medium, 4. High, 5. Severe)
Regression impact is the impact to the existing business processes and functions and is weighted very heavily in terms of the overall determination of the test effectiveness required. This is also the most important focus of the service validation and test group.
- A. Changes to high risk areas
- B. Changes to highly integrated areas (same code is shared by multiple business units/processes etc)
- C. Lack of clear definition of the scope of changes (like support packs without clear release notes etc)
- D. Scope of regression based on the change
4. Determine Recovery Effort/Difficulty from Potential Failure (1. Min, 2. Low, 3. Medium, 4. High, 5. Severe)
When determining the test effectiveness required to mitigate the risk of the change, the ability to recover from a potential failure needs to be considered. Even if a failure occurs, if recovery is possible quickly, then the risk is mitigated to an extent. However, if recovery is very difficult then the test effectiveness needs to be high if the solution component is critical to operations.
- A. Existence of work around if potential failure occurs
- B. Existence of back out procedure and ease of performing back outs
- C. Ability and turnaround time to fix problems in case of failure
- D. Is the failure reflected real time or is it more batch oriented
- E. Existence of alerts or early warning indicators to aid proactive intervention
Risk Based Testing – An Example:

Prolifics specializes in providing end-to-end testing and test automation solutions that are backed by a unique service framework, proven test accelerators and one of the highest defect removal efficiency rate in the industry. Our highly skilled team of testing specialists help to enhance IT productivity and improve application quality, saving millions of dollars through early detection and scope coverage.
To learn more, visit http://www.prolifics.com/quality-assurance-testing.
|
|
Jagan Erra is a Delivery Manager in the Testing Practice at Prolifics. With over 15 years of experience, Jagan has a proven ability to identify, analyze and solve problems to increase customer satisfaction and control costs through expertise in program development and management, IT quality processes, models - ITIL, ISO, client training and cross-functional team leadership.
|
Wednesday, July 23, 2014
Client Showcase: Retailer Better Meets Customer Needs with Managed Services
Prolifics is committed to helping our clients create (and grow) competitive advantage in their industry. We are proud to have empowered this well known Retailer to do just that, again. After a successful e-commerce solution, Prolifics and our client teamed up again to bring ongoing managed services to further differentiate from the competition.
Our client is a high-end department store chain based in the United Kingdom. Business leaders previously began a strategic initiative to expand the Company’s e-commerce capabilities by expanding the product lines available online and improving connectivity with their distribution service to shorten delivery times in support of a higher volume of online purchases. Prolifics successfully led the implementation of a centralized Warehouse Management System (WMS) that would serve as the foundation for this project. The Prolifics team continued to provide support as needed to deliver the necessary IBM WebSphere MQ and IBM Integration Bus skills required to troubleshoot issues and make updates within the system. Over time, the Company found that their internal IT staff was spending approximately 60% of their time supporting the WMS production environment rather than deepening the capabilities of the solution. Finally, as ad hoc support service costs for the solution began to balloon during the holiday season, their busiest season for online purchases, business leaders began to explore better long-term support options with Prolifics. Valuing the deep technical expertise Prolifics has with IBM WebSphere MQ and IBM Integration Bus, our client engaged the Prolifics team to provide ongoing managed services in order to effectively maintain their WMS system while releasing internal staff to focus on other critical business issues. Prolifics recommended the implementation of SmartCloud APM and SmartCloud Control Desk to enable real-time alerts and provide a centralized ticketing system for submitting and addressing IT issues. Prolifics experts then led the implementation of these tools and developed reasonable service level agreements (SLAs) for the ongoing services that would meet the Company's needs. With managed services now in place, the Company is assured of timely, knowledgeable support for the more than 50 workflows in their WMS solution, with dedicated Prolifics staff available during regular call center hours to rapidly address issues and provide development support as needed. Further, with the new monitoring tools in place, staff can more proactively identify and address potential failures to ensure functionality and ultimately create a better user experience for online consumers.
To learn more about Prolifics Managed Services, visit: http://www.prolifics.com/managed-services
Our client is a high-end department store chain based in the United Kingdom. Business leaders previously began a strategic initiative to expand the Company’s e-commerce capabilities by expanding the product lines available online and improving connectivity with their distribution service to shorten delivery times in support of a higher volume of online purchases. Prolifics successfully led the implementation of a centralized Warehouse Management System (WMS) that would serve as the foundation for this project. The Prolifics team continued to provide support as needed to deliver the necessary IBM WebSphere MQ and IBM Integration Bus skills required to troubleshoot issues and make updates within the system. Over time, the Company found that their internal IT staff was spending approximately 60% of their time supporting the WMS production environment rather than deepening the capabilities of the solution. Finally, as ad hoc support service costs for the solution began to balloon during the holiday season, their busiest season for online purchases, business leaders began to explore better long-term support options with Prolifics. Valuing the deep technical expertise Prolifics has with IBM WebSphere MQ and IBM Integration Bus, our client engaged the Prolifics team to provide ongoing managed services in order to effectively maintain their WMS system while releasing internal staff to focus on other critical business issues. Prolifics recommended the implementation of SmartCloud APM and SmartCloud Control Desk to enable real-time alerts and provide a centralized ticketing system for submitting and addressing IT issues. Prolifics experts then led the implementation of these tools and developed reasonable service level agreements (SLAs) for the ongoing services that would meet the Company's needs. With managed services now in place, the Company is assured of timely, knowledgeable support for the more than 50 workflows in their WMS solution, with dedicated Prolifics staff available during regular call center hours to rapidly address issues and provide development support as needed. Further, with the new monitoring tools in place, staff can more proactively identify and address potential failures to ensure functionality and ultimately create a better user experience for online consumers.
To learn more about Prolifics Managed Services, visit: http://www.prolifics.com/managed-services
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)










